WHAT IS BCC CANCER?
Basal cell cancer, also called BCC or basal cell carcinoma, is a type of skin cancer. It is the most common type of skin cancer, but fortunately, usually the least dangerous. Basal cells are found in the deepest layer of the epidermis (the outermost layer of the skin) and BCC cancer is the uncontrolled and abnormal growth that arise in the skin’s basal cells. It can look like open sores, pink growths, shiny bumps or scars, or red patches.
Cumulative and intense sun exposure usually causes BCC cancer. Thankfully, basal cell carcinomas rarely spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. However, they should not be left untreated as they can damage the skin and surrounding tissue.
It is important to get skin checks regularly by a qualified skin specialist. If you are looking for BCC skin cancer treatment in Brisbane, contact us so our team can discuss your treatment options.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF BCC CANCER?
There are more than 20 different types of histological growth patterns of BCC. Some of these include:
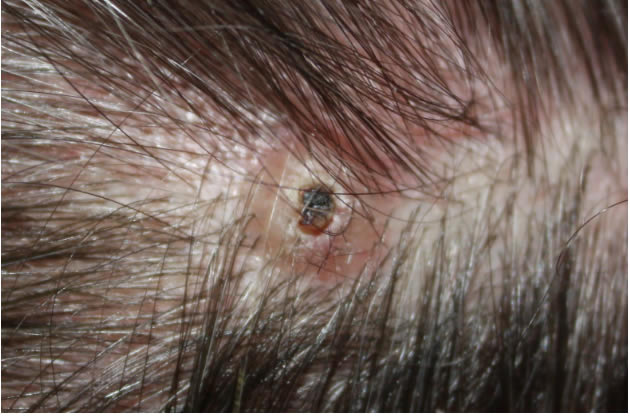
Nodular BCC
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma is the most common type of BCC cancer and presents itself as nodules on the skin, usually in the head and neck area.
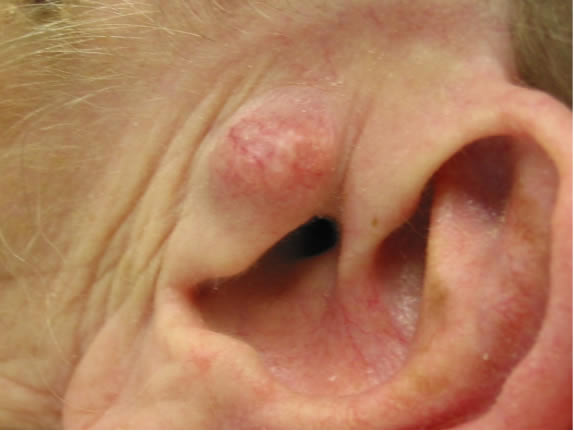
Superficial BCC
This type of BCC cancer is most common in younger adults and appears on upper trunk and shoulders of an individual, but may be found on the face. It can present as a red patch similar to eczema.
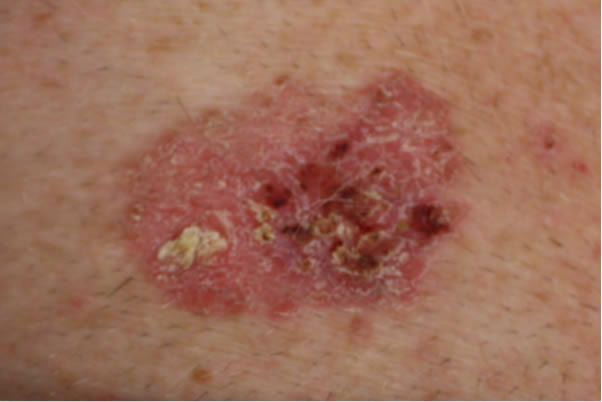
Infiltrating or Morphoeic BCC
These types of BCC can present as skin thickening or scar tissue making diagnosis more challenging.
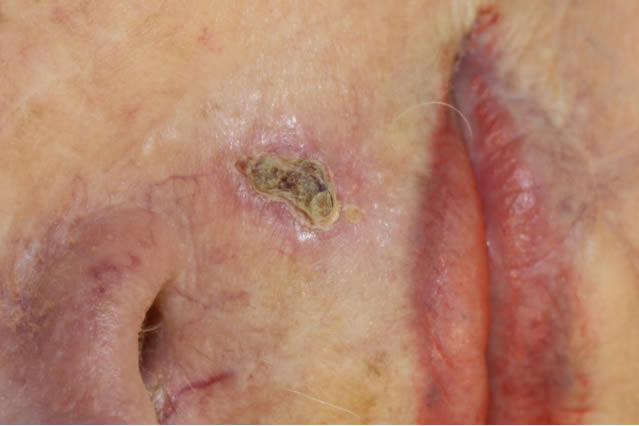
Basosquamous Carcinoma
Basosquamous carcinoma is a mix of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. This has the potential to be more aggressive than other forms of BCC.
WHAT CAUSES BCC CANCER?
The damage caused by long-term sun exposure over your lifetime and occasional extended, intense exposure (typically leading to sunburn) can lead to BCC. The DNA mutations present in BCCs may be caused by ultraviolet radiation (sun) exposure.
There has been cases that contact with arsenic, exposure to radiation, or complications of burns, scars, infections, vaccinations, or even tattoos have contributed to BCC. Both inherited and acquired genetic defects can predispose to BCC development.
What are the risk factors for developing BCC cancer and how to reduce the risks?
Minimising your UV exposure and taking sun safety seriously can help prevent BCC cancer. This type of cancer is very rarely life-threatening, so early detection can reduce the severity. Make sure to have a qualified dermatologist such as Dr Hills, examine your skin regularly for any early signs of BCC so it can be treated appropriately.
WHAT DOES BCC CANCER LOOK LIKE?
BCC can come in various shapes and sizes. You may see a dome-shaped skin growth with visible vessels on your skin. This type of BCC is often pink or skin colored. However, it can also be brown or black. This type of BCC can grow very slowly. It can be flat in the centre and ooze and crust over. It also is susceptible to bleeding. They can also be shiny with red patches, waxy, hard and pale, or a scar-like yellow growth.
HOW IS BCC CANCER DIAGNOSED?
Your dermatologist will usually be able to clinically diagnose a BCC, however the only way to diagnose any skin cancer if not clinically apparent, including basal cell cancer or basal cell carcinoma, is with a skin biopsy. Your trusted dermatologist can perform a skin biopsy for you during office visits. Your dermatologist will remove a part of your growth or the entire growth and send it to a laboratory to be tested. If the results indicate that you have BCC, your dermatologist will determine which course of treatment is best for you.
HOW IS BCC CANCER TREATED?
There are many treatments used for basal cell carcinoma removal. Your dermatologist will recommend the best treatment for you depending on your biopsy results, the site and size of the BCC.
Treatments for BCC cancer can include:
Excision – This is a simple surgical procedure with no life-threatening risks. During your office visit, your dermatologist will numb the affected area and remove any tumour and some healthy looking skin around a tumour. The importance of eliminating some normal skin from around a tumour is to make sure the healthy skin is free of cancer. The dermatologist checks this by sending the removed skin and healthy skin to the laboratory to be tested just like a biopsy.
Curettage and electrodesiccation – This treatment has two steps and is mainly used for superficial BCC. During the first step, the dermatologist scraps away the tumour. In the second step, electricity is used to destroy any remaining BCC cells at the base.
Mohs surgery – Mohs micrographic surgery has the highest cure rate and is used for people with an aggressive subtype of BCC, poorly defined BCC or in high risk areas on the head and neck. During this treatment, the Mohs Specialist will remove the growth and some normal skin around the tumour. The doctor will check the normal skin under a microscope for any cancer signs. This procedure of removing tissue and testing for cancer cells continues until the dermatologist is sure that you are BCC cancer free. The area may need reconstruction with a skin flap or graft to achieve the best cosmetic outcome.
Photodynamic therapy – Is primarily used to treat superficial and small nodular BCC. This treatment involves application of ALA solution to the BCC and surrounding tissue followed by illumination of the area at least three hours later to photoactivate the active ingredient in the cream to destroy the tumour cells. Two treatments are required 7-14 days apart. Generally very good cosmetic results are achieved.
Cryotherapy – Liquid nitrogen cryotherapy is used in a double freeze thaw cycle to destroy superficial BCC. This commonly results in permanent lightening of the skin in the treated area.
Fluorouracil – Is a topical chemotherapy agent applied to superficial tumours. It needs to be used for a prolonged period and results in significant inflammation at the site of application. There is also a high recurrence rate with this treatment.
Imiquimod – This is a topical cream which is applied for many weeks to up regulate the patient’s own immune response to fight a superficial BCC. Significant inflammation can occur with this treatment as well which may result in scarring.
Radiotherapy – Is mainly used in patient’s who are unsuitable for surgery or as an adjunctive treatment in very aggressive BCC skin cancer which may have invaded nerves in the skin. The treatment course is prolonged over many weeks and results in a significant healing episode which can lead to long term scarring.
Aesthetix is experienced in these procedures for BCC skin cancer treatment in Brisbane, so contact us to discuss your treatment options.
HOW SUCCESSFUL IS BCC CANCER TREATMENT?
The goal of any cancer treatment is to try to remove the cancer completely with the least possible cosmetic damage. Early detection and treatment can see a very low incidence of the cancer returning making BCC cancer treatment in most cases successful. As noted above in the treatment options some have better cure rates than others and better cosmetic outcomes.
WHAT CAN BE EXPECTED AFTER BCC CANCER SURGERY?
Depending on the extent of your surgery it is not unusual to experience a variable amount of swelling and bruising which usually resolve over one to two weeks. You will be required to attend for at least one post operative visit to assess your healing and the wound and for suture removal if needed.
Make sure you regularly visit your dermatologist to make sure you are healing correctly and to minimize the risk of recurrence. Dr Hills will advise follow up frequency after your treatment is completed.
READY TO DISCUSS BCC CANCER REMOVAL?
For a confidential discussion on our BCC cancer removal procedures, please contact us on 07 3720 8788 or make an enquiry online. We look forward to speaking with you.

NEW Sunscreen Product
Dr Hills has developed a Zinc Oxide sunscreen containing no chemical sunscreen. Our Aesthetix Sunscreen is available in standard and tinted, and is available for purchase at Dr Hills rooms or you can buy it from our online shop.
 Dr Russell Hills is an experienced cosmetic dermatologist based in Brisbane, Australia and is a member of the Academy of Facial Plastic Surgery. Dr Hills also has extensive experience in MOHS surgery for skin cancer removal, and is the principal Dermatologist at Aesthetix.
Dr Russell Hills is an experienced cosmetic dermatologist based in Brisbane, Australia and is a member of the Academy of Facial Plastic Surgery. Dr Hills also has extensive experience in MOHS surgery for skin cancer removal, and is the principal Dermatologist at Aesthetix.
Dr Hills regularly lectures on cosmetic and laser surgery and skin cancer removal, and has numerous publications on these topics. He is a member of a number of Australian and American medical associations, and attends local and international conferences to stay up-to-date with the latest approaches in cosmetic medicine.
Adherence to the information on this site will not ensure successful treatment in every situation and will not ensure specific results in the individual patient. Although complications may be rare, there are certain inherent risks connected with surgical procedures that should be discussed with the dermatologist. This Website contains very general information and any procedures mentioned in it should be discussed in detail with your dermatologist at the time of consultation.
